Where Do You Lose Weight First?
There are various reasons why people want to lose weight: for health, enhanced performance,...
Types of Bariatric Procedures
Weight Loss Surgery Options Discover all...
Understanding Weight-Loss Surgery: Is it for you?
Weight loss surgery or bariatric surgery...
Risks of Bariatric Surgery
What are the Risks of Bariatric...
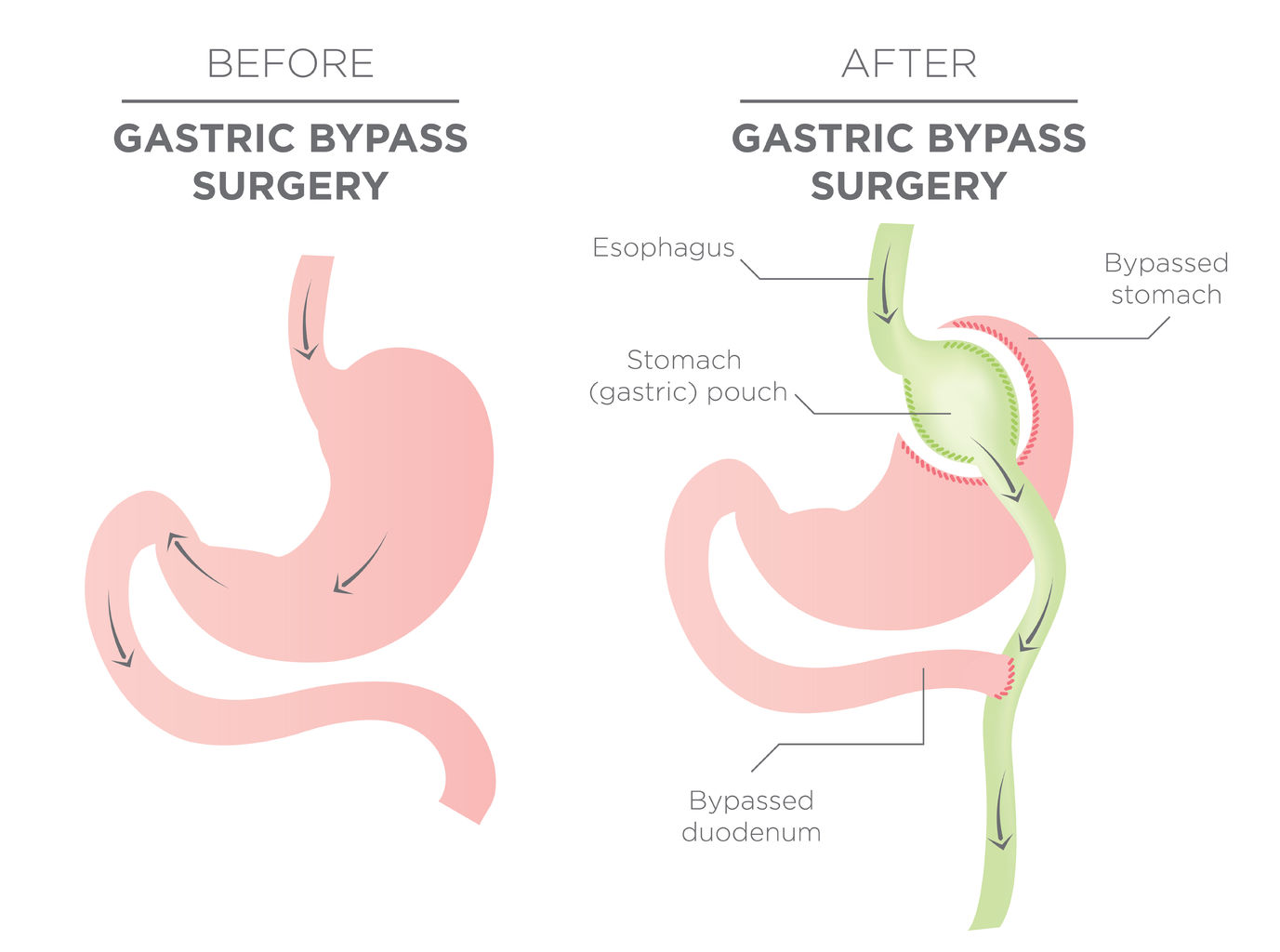
Gastric Bypass
View AllGastric Bypass Scars
Most weight loss surgeries are currently...
Am I a Candidate for Gastric Bypass Surgery
Obesity with its associated comorbid conditions...
Gastric Bypass Alternatives
Surgical treatment of obesity is currently...
Gastric Sleeve
View AllRecovery from Gastric Sleeve – What to Expect from Day 1
Recovery is gradual after gastric sleeve...
Will Your Stomach Stretch after Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
Temporary stretching of the stomach is...
Other Articles
How to Prepare for Safe Weight Loss Surgery
In any scheduled an elective procedure, it is always recommended that you familiarize yourself...
Bariatric Surgery Statistics, Facts
Weight loss surgery is a proven option for obese and morbidly obese individuals...
Bariatric Surgery Diet Guide
The development of obesity is the result of interaction between genetic make-up of an...
Bariatric Surgery 101 Guide: Read This First
The complete patient’s guide to bariatric surgery. Learn more about surgical weight loss, and your options for success. Bariatric...
Why Don’t More People Get Bariatric Surgery?
Obesity rates are rising. However, bariatric surgery utilization remains low. For over five decades surgeons have used procedures that...
Joint Pain After Bariatric Surgery: What the Studies Show
Many people who are overweight or obese suffer from health complications, including a high instance of obesity-related joint pain....
Why Do I Need a Psychological Evaluation Before Bariatric Surgery?
Weight loss surgery provides an opportunity for people to change their lives. It seems like the ideal opportunity to...
How Many are Eligible for Bariatric Surgery?
Obesity rates are rising. However, bariatric surgery utilization remains low. For over five decades surgeons have used procedures that...
17 Alternative Ways to Pay for Weight Loss Surgery
When obesity begins to overwhelm aspects of your life, it’s time to do something about it. Diet and exercise...
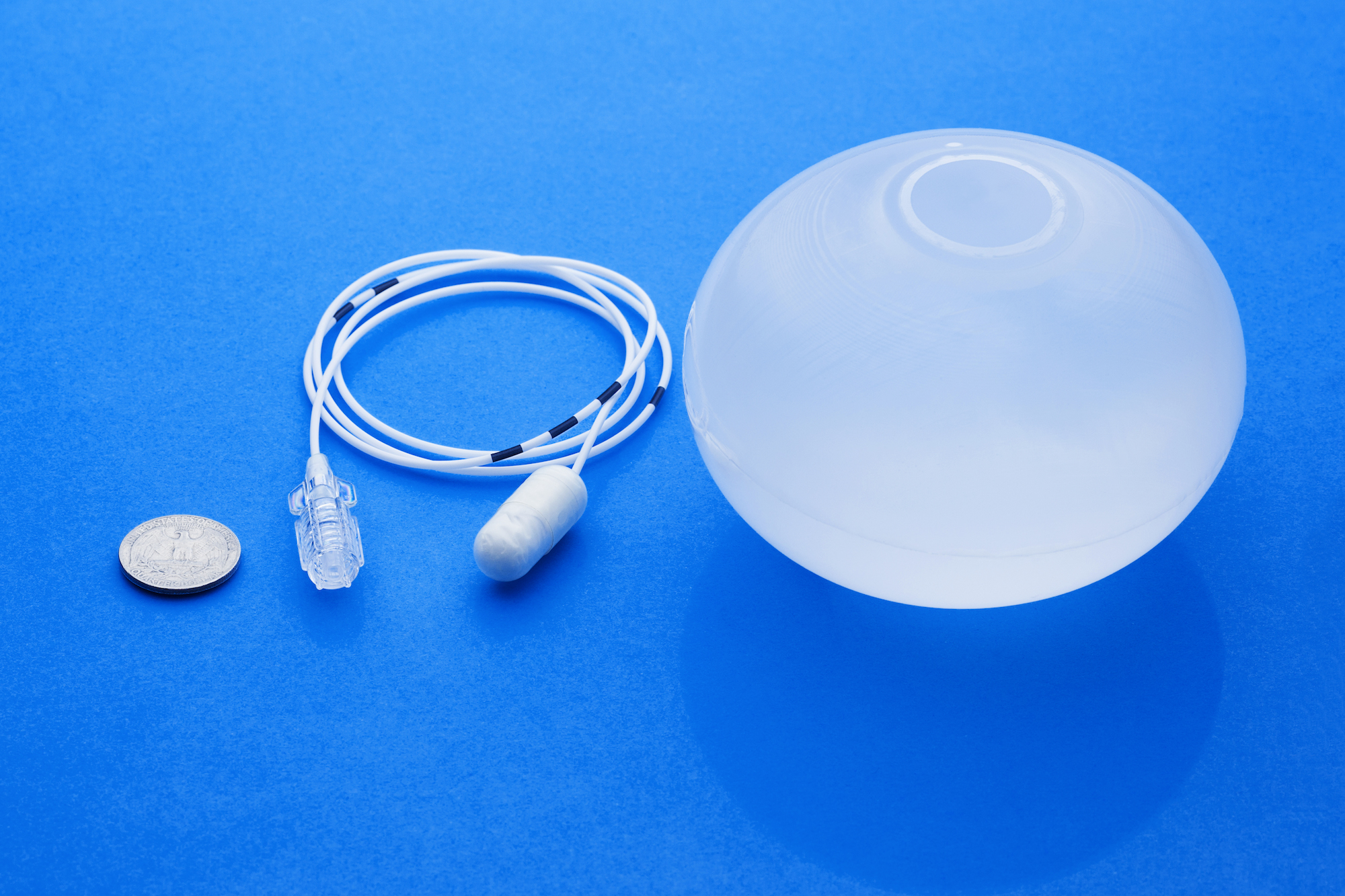
Belly Balloon: (Previously Obalon) How it Works, Requirements, Cost
Belly Balloon, previously called Obalon Gastric Balloon is a swallowable weight loss system or gastric balloon. Unlike most of...
Guide to Weight Loss Surgery Grants
Obesity is a prevalent societal problem as well as an individual challenge. The percentage of the population dealing with obesity continues...
Elipse Gastric Balloon: Swallowable, NonSurgical Weight Loss Treatment
Elipse is one variation of the gastric balloon that has yet to be approved by the FDA. With this...
How Safe Is Gastric Sleeve Surgery in Tijuana, Mexico?
Are you looking for statistics on the safety of gastric sleeve surgery in Mexico? As a patient, you have...
Bariatric Surgery Certifications, Credentials Explained
Bariatric surgery can be defined as typical weight loss surgery that allows an obese person to control his/her body...
How to Choose a Bariatric Surgeon
Weight loss surgery, or bariatric surgery, becomes the only option to treat obesity in some patients. The choice of...
How Important are Bariatric Surgery Support Groups?
Undergoing bariatric surgery to lose body fat can be overwhelming, both emotionally and physically. The weight loss journey can...
10 Things Your Doctor Won’t Tell You About Weight Loss Surgery
If you have your mindset on bariatric surgery, you must be consulting a physician or surgeon. Weight loss surgery...
Review: Prosper Healthcare Lending – Should You Choose it for Bariatric Surgery Financing?
Bariatric surgery has emerged as a popular trend today, helping restore health and happiness in people with obesity and...
Review: eFinancing Solutions: Is It a Good Choice to Finance Your Bariatric Surgery?
As obesity and associated co-morbidities continue to wreak havoc on one’s health and overall wellbeing, bariatric surgery is sparking...
Review: United Medical Credit for Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric procedures are essential for significantly overweight people who have failed to lose weight despite all efforts. Such surgery...
Review: Citerra Finance for Bariatric Surgery
Citerra Finance is one of the few financing companies that cover bariatric surgery. The company is best known for...
Protein Intake after Bariatric Surgery – How to Get Enough Protein
Bariatric surgery should be seen as a means to an end and not the end in itself. Diet still...
Medical Necessity Letters for Weight Loss Surgery
Each person deserves the fundamental rights and access to healthcare. However, every so often, you will find an individual...
Weight Loss Surgery Insurance Appeal Letter & The Appeals Process
Weight Loss Surgery Insurance Appeal Guide There are several reasons why your weight loss surgery claim may be denied....
The Best Apps for Bariatric Surgery
After one has been able to take the brave and bold step of having bariatric surgery in order to...